3.avi_open2()
该函数用于打开FFmpeg的输入输出文件。avio_open2()的声明位于libavformat\avio.h文件中
/** * Create and initialize a AVIOContext for accessing the * resource indicated by url. * @note When the resource indicated by url has been opened in * read+write mode, the AVIOContext can be used only for writing. * * @param s Used to return the pointer to the created AVIOContext. * In case of failure the pointed to value is set to NULL. * @param url resource to access * @param flags flags which control how the resource indicated by url * is to be opened * @param int_cb an interrupt callback to be used at the protocols level * @param options A dictionary filled with protocol-private options. On return * this parameter will be destroyed and replaced with a dict containing options * that were not found. May be NULL. * @return >= 0 in case of success, a negative value corresponding to an * AVERROR code in case of failure */ int avio_open2(AVIOContext **s, const char *url, int flags, const AVIOInterruptCB *int_cb, AVDictionary **options);avio_open2()函数参数的含义如下:
- s:函数调用成功之后创建的AVIOContext结构体。
- url:输入输出协议的地址(文件也是一种“广义”的协议,对于文件来说就是文件的路径)。
- flags:打开地址的方式。可以选择只读,只写,或者读写。取值如下。
- AVIO_FLAG_READ:只读。
- AVIO_FLAG_WRITE:只写。
- AVIO_FLAG_READ_WRITE:读写。
- int_cb:目前还没有用过。
- options:目前还没有用过。
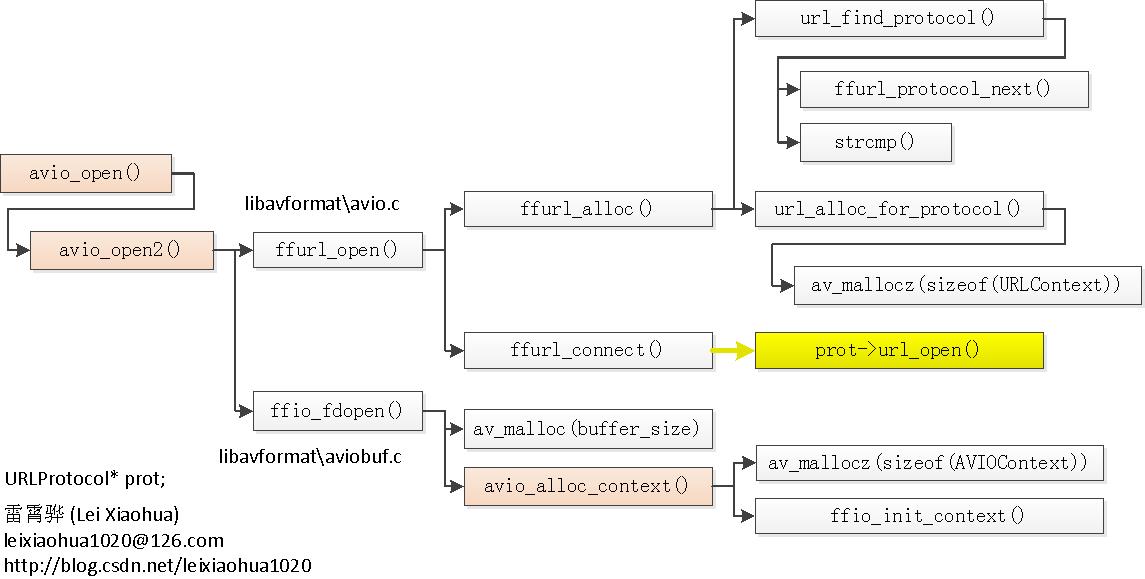
函数调用过程
源码:
int avio_open2(AVIOContext **s, const char *filename, int flags,
const AVIOInterruptCB *int_cb, AVDictionary **options)
{
URLContext *h;
int err;
err = ffurl_open(&h, filename, flags, int_cb, options);
if (err < 0)
return err;
err = ffio_fdopen(s, h);
if (err < 0) {
ffurl_close(h);
return err;
}
return 0;
}
它主要调用了2个函数:ffurl_open()和ffio_fdopen()。
- 其中ffurl_open()用于初始化URLContext
- ffio_fdopen()用于根据URLContext初始化AVIOContext。URLContext中包含的URLProtocol完成了具体的协议读写等工作。AVIOContext则是在URLContext的读写函数外面加上了一层“包装”(通过retry_transfer_wrapper()函数)
ffurl_open()
int ffurl_open(URLContext **puc, const char *filename, int flags,
const AVIOInterruptCB *int_cb, AVDictionary **options)
{
int ret = ffurl_alloc(puc, filename, flags, int_cb);
if (ret < 0)
return ret;
if (options && (*puc)->prot->priv_data_class &&
(ret = av_opt_set_dict((*puc)->priv_data, options)) < 0)
goto fail;
if ((ret = av_opt_set_dict(*puc, options)) < 0)
goto fail;
ret = ffurl_connect(*puc, options);
if (!ret)
return 0;
fail:
ffurl_close(*puc);
*puc = NULL;
return ret;
}
ffurl_open()主要调用了2个函数:ffurl_alloc()和ffurl_connect()。ffurl_alloc()用于查找合适的URLProtocol,并创建一个URLContext;ffurl_connect()用于打开获得的URLProtocol
ffurl_alloc()
int ffurl_alloc(URLContext **puc, const char *filename, int flags,
const AVIOInterruptCB *int_cb)
{
URLProtocol *p = NULL;
if (!first_protocol) {
av_log(NULL, AV_LOG_WARNING, "No URL Protocols are registered. "
"Missing call to av_register_all()?\n");
}
p = url_find_protocol(filename);
if (p)
return url_alloc_for_protocol(puc, p, filename, flags, int_cb);
*puc = NULL;
if (av_strstart(filename, "https:", NULL))
av_log(NULL, AV_LOG_WARNING, "https protocol not found, recompile with openssl or gnutls enabled.\n");
return AVERROR_PROTOCOL_NOT_FOUND;
}
从代码中可以看出,ffurl_alloc()主要调用了2个函数:
- url_find_protocol()根据文件路径查找合适的URLProtocol
- url_alloc_for_protocol()为查找到的URLProtocol创建URLContext。
url_find_protocol()
#define URL_SCHEME_CHARS \
"abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz" \
"ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ" \
"0123456789+-."
static struct URLProtocol *url_find_protocol(const char *filename)
{
URLProtocol *up = NULL;
char proto_str[128], proto_nested[128], *ptr;
size_t proto_len = strspn(filename, URL_SCHEME_CHARS);
if (filename[proto_len] != ':' &&
(filename[proto_len] != ',' || !strchr(filename + proto_len + 1, ':')) ||
is_dos_path(filename))
strcpy(proto_str, "file");
else
av_strlcpy(proto_str, filename,
FFMIN(proto_len + 1, sizeof(proto_str)));
if ((ptr = strchr(proto_str, ',')))
*ptr = '\0';
av_strlcpy(proto_nested, proto_str, sizeof(proto_nested));
if ((ptr = strchr(proto_nested, '+')))
*ptr = '\0';
while (up = ffurl_protocol_next(up)) {
if (!strcmp(proto_str, up->name))
break;
if (up->flags & URL_PROTOCOL_FLAG_NESTED_SCHEME &&
!strcmp(proto_nested, up->name))
break;
}
return up;
}
url_find_protocol()函数表明了FFmpeg根据文件路径猜测协议的方法。该函数首先根据strspn()函数查找字符串中第一个“非字母或数字”的字符的位置,并保存在proto_len中。一般情况下,协议URL中都是包含“:”的,比如说RTMP的URL格式是“rtmp://xxx…”,UDP的URL格式是“udp://…”,HTTP的URL格式是“http://...”。因此,一般情况下proto_len的数值就是“:”的下标(代表了“:”前面的协议名称的字符的个数,例如rtmp://的proto_len为4)。 接下来函数将filename的前proto_len个字节拷贝至proto_str字符串中。 PS: 这个地方比较纠结,源代码中av_strlcpy()函数的第3个参数size写的字符串的长度是(proto_len+1),但是查了一下av_strlcpy()的定义,发现该函数至多拷贝(size-1)个字符。这么一涨一消,最终还是拷贝了proto_len个字节。例如RTMP协议就拷贝了“rtmp”,UDP协议就拷贝了“udp”。
这里有一种例外,那就是文件路径。“文件”在FFmpeg中也是一种“协议”,并且前缀是“file”。也就是标准的文件路径应该是“file://...”格式的。但是这太不符合我们一般人的使用习惯,我们一般是不会在文件路径前面加上“file”协议名称的。所以该函数采取的方法是:一旦检测出来输入的URL是文件路径而不是网络协议,就自动向proto_str中拷贝“file”。 其中判断文件路径那里有一个很复杂的if()语句。根据我的理解,“||”前面的语句用于判断是否是相对文件路径,“||”后面的语句用于判断是否是绝对路径
ffurl_connect()
ffurl_connect()用于打开获得的URLProtocol
int ffurl_connect(URLContext *uc, AVDictionary **options)
{
int err =
uc->prot->url_open2 ? uc->prot->url_open2(uc,
uc->filename,
uc->flags,
options) :
uc->prot->url_open(uc, uc->filename, uc->flags);
if (err)
return err;
uc->is_connected = 1;
/* We must be careful here as ffurl_seek() could be slow,
* for example for http */
if ((uc->flags & AVIO_FLAG_WRITE) || !strcmp(uc->prot->name, "file"))
if (!uc->is_streamed && ffurl_seek(uc, 0, SEEK_SET) < 0)
uc->is_streamed = 1;
return 0;
}
该函数最重要的函数就是它的第一句:URLProtocol中是否包含url_open2()?如果包含的话,就调用url_open2(),否则就调用url_open()。 url_open()本身是URLProtocol的一个函数指针,这个地方根据不同的协议调用的url_open()具体实现函数也是不一样的,例如file协议的url_open()对应的是file_open(),而file_open()最终调用了_wsopen(),_sopen()(Windows下)或者open()(Linux下,类似于fopen())这样的系统中打开文件的API函数;而libRTMP的url_open()对应的是rtmp_open(),而rtmp_open()最终调用了libRTMP的API函数RTMP_Init(),RTMP_SetupURL(),RTMP_Connect() 以及RTMP_ConnectStream()
ffio_fdopen()
ffio_fdopen()使用已经获得的URLContext初始化AVIOContext
#define IO_BUFFER_SIZE 32768
int ffio_fdopen(AVIOContext **s, URLContext *h)
{
uint8_t *buffer;
int buffer_size, max_packet_size;
max_packet_size = h->max_packet_size;
if (max_packet_size) {
buffer_size = max_packet_size; /* no need to bufferize more than one packet */
} else {
buffer_size = IO_BUFFER_SIZE;
}
buffer = av_malloc(buffer_size);
if (!buffer)
return AVERROR(ENOMEM);
*s = avio_alloc_context(buffer, buffer_size, h->flags & AVIO_FLAG_WRITE, h,
(void*)ffurl_read, (void*)ffurl_write, (void*)ffurl_seek);
if (!*s) {
av_free(buffer);
return AVERROR(ENOMEM);
}
(*s)->direct = h->flags & AVIO_FLAG_DIRECT;
(*s)->seekable = h->is_streamed ? 0 : AVIO_SEEKABLE_NORMAL;
(*s)->max_packet_size = max_packet_size;
if(h->prot) {
(*s)->read_pause = (int (*)(void *, int))h->prot->url_read_pause;
(*s)->read_seek = (int64_t (*)(void *, int, int64_t, int))h->prot->url_read_seek;
}
(*s)->av_class = &ffio_url_class;
return 0;
}
ffio_fdopen()函数首先初始化AVIOContext中的Buffer。如果URLContext中设置了max_packet_size,则将Buffer的大小设置为max_packet_size。如果没有设置的话(似乎大部分URLContext都没有设置该值),则会分配IO_BUFFER_SIZE个字节给Buffer。IO_BUFFER_SIZE取值为32768
avio_alloc_context()
ffio_fdopen()接下来会调用avio_alloc_context()初始化一个AVIOContext。avio_alloc_context()本身是一个FFmpeg的API函数
/**
* Allocate and initialize an AVIOContext for buffered I/O. It must be later
* freed with av_free().
*
* @param buffer Memory block for input/output operations via AVIOContext.
* The buffer must be allocated with av_malloc() and friends.
* @param buffer_size The buffer size is very important for performance.
* For protocols with fixed blocksize it should be set to this blocksize.
* For others a typical size is a cache page, e.g. 4kb.
* @param write_flag Set to 1 if the buffer should be writable, 0 otherwise.
* @param opaque An opaque pointer to user-specific data.
* @param read_packet A function for refilling the buffer, may be NULL.
* @param write_packet A function for writing the buffer contents, may be NULL.
* The function may not change the input buffers content.
* @param seek A function for seeking to specified byte position, may be NULL.
*
* @return Allocated AVIOContext or NULL on failure.
*/
AVIOContext *avio_alloc_context(
unsigned char *buffer,
int buffer_size,
int write_flag,
void *opaque,
int (*read_packet)(void *opaque, uint8_t *buf, int buf_size),
int (*write_packet)(void *opaque, uint8_t *buf, int buf_size),
int64_t (*seek)(void *opaque, int64_t offset, int whence));
avio_alloc_context()看上去参数很多,但实际上并不复杂。先简单解释一下它各个参数的含义:
- buffer:AVIOContext中的Buffer。
- buffer_size:AVIOContext中的Buffer的大小。
- write_flag:设置为1则Buffer可写;否则Buffer只可读。
- opaque:用户自定义数据。
- read_packet():读取外部数据,填充Buffer的函数。
- write_packet():向Buffer中写入数据的函数。
- seek():用于Seek的函数。 该函数成功执行的话则会返回一个创建好的AVIOContext。
ffurl_read(),ffurl_write(),ffurl_seek() 现在我们再回到ffio_fdopen(),会发现它初始化AVIOContext的结构体的时候,首先将自己分配的Buffer设置为该AVIOContext的Buffer;然后将URLContext作为用户自定义数据(对应AVIOContext的opaque变量)提供给该AVIOContext;最后分别将3个函数作为该AVIOContext的读,写,跳转函数:ffurl_read(),ffurl_write(),ffurl_seek()